Faster Re-translation Using Non-Autoregressive Model For Simultaneous Neural Machine Translation
使用 非自回归方法+重译 , 降低了同传系统的计算开销, 对重译提出了新的metric(指标)
-
为什么用非自回归:
- We choose the LevT model as our decoder since it is a non-autoregressive neural language model and suits the re-translation objective of editing the partial translation(适合重译与修改)
- The model with these modified placeholder and deletion classifiers focuses more on appending the partial translation whenever new source information comes in, which results in smoother translation having lower textual instability. (可以重复修改,更加平滑与稳定)
-
非自回归Transformer (LevT)
- The LevT model parallelly generates all the tokens in the translation and iteratively modifies the translation by using insertion/deletion operations. These operations are achieved by employing Placeholder classifier, Token Classifier, and Deletion Classifier components in the Transformer decoder.(迭代地插入删除操作,占位符分类器、Token分类器、删除分类器)
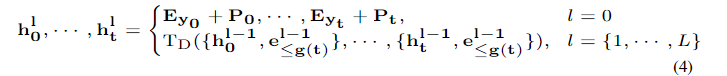 TD代表一层Decoder,可以看出每一个位置的隐状态都是被独立计算的,共计t个位置(t 根据输入动态增加)
TD代表一层Decoder,可以看出每一个位置的隐状态都是被独立计算的,共计t个位置(t 根据输入动态增加)- 最后一层的隐状态被输入三个分类器中,得到一次结果,再迭代地插入删除。
-
占位符分类器:
- It predicts the number of tokens to be inserted between every two tokens in the current partial translation(预测每两个Token之间可能被插入的字符数目)
- 输入:Decoder最后一层的位置 i 与 位置 i + 1 的隐状态表示 + 位置偏移
- 输出:第 i 个位置被插入的字符(φ)数目
-
Token分类器:
- it fills in tokens for all the placeholders inserted by the placeholder classifier. (填充占位符)
- 相当于在位置 i 做一次inference
-
删除分类器:
- predicts whether to keep(1) or delete(0) each token in the (partial) translation. (预测每一个位置是否删除)
- 输入: 第 i 个位置的Decoder最后一层的隐状态 + 位置偏移
- 输出: keep(0) or delete(1)
-
ReTranslation稳定性分析
- One important property of the re-translation based models is that they should produce the translation output with as few textual instabilities or flickers as possible(采用重译的方法,要尽可能减少抖动)
- we suggest a new stability measure metric, called Normalized Click-N-Edit (NCNE)
收获:
- 非自回归+SiMT的思路,而且效果不错。
- 了解了非自回归的大致原理
问题:
- 非自回归的优势与劣势?(推理速度 与 计算开销 可以平衡吗)
It Is Not As Good As You Think! Evaluating Simultaneous Machine Translation on Interpretation Data
使用真实交互输入进行测试,而不是离线翻译语料,结果差异较大。然而目前交互数据很少,本文提出了Translation2Interpretation方法将普通译文转化为交互式的风格作为训练数据集,在交互式测试中得到了提升。
-
交互式数据如何刻画与评估?
交互式数据 (指的就是ASR得出的文本,没有分词,没有纠错
There are two stages in our human annotation process: 1) segmentation; 2) ASR error correction. You can find our Interpretation test sets after each stage in
noised-interpretationandclean-interpretation, respectively. The corresponding Translation test set can be found inclean-translation.
-
交互式数据与离线翻译语料的差异,以及这些差异为什么会导致翻译质量的下降?
交互式数据没有分词与纠错,这种Raw data 的结果必然效果不如Clean data的结果。
-
如何更好地处理交互式数据?
从训练数据集的角度出发,将大量的离线翻译文本 转化为 稀缺的交互文本作为训练集,得到一个适应交互式输入的模型。
To bridge the gap, we proposed a data augmentation style transfer technique to create parallel pseudo-interpretations from abundant offline translation data (Translation Style 2 Interpretation Style)
收获:
- 同传目前的Text2Text方向的研究,离传统翻译较近,但是与真实场景相差较大,尤其是数据集上。目前缺少这种交互式的文本翻译数据集。Speech2Text 更加贴近现实。
A Generative Framework for Simultaneous Machine Translation
读写策略 + 泊松分布 ; 正在开源(没有找到开源)
Our proposed generative simultaneous machine translation model (GSiMT) integrates out all the hypothesises by a dynamic programming algorithm (Algorithm 1) with the help of the introduced latent variable.
补充:泊松分布:
当时主要的问题是预测未来中发生事件的次数,更正式地说,预测在固定间隔的时间里,预测该事件发生n次的概率。
